Labiaplasty is a surgical procedure usually done to reduce the size of your labia minora — skin folds that surround your urethra and vagina. Excess skin can get twisted and pinched, causing discomfort during exercise, physical activities and intercourse. You may also have labiaplasty for cosmetic reasons or as part of gender-affirming surgery.

What is labiaplasty?
Labiaplasty is a surgical procedure that alters the size of the labia, typically to reduce physical discomfort or as part of gender-affirming surgery. The labia are the skin folds surrounding the vagina, consisting of the outer labia majora and inner labia minora. During labiaplasty, a surgeon may remove tissue to reduce size, inject fillers to enlarge, or reconstruct the labia using other tissue. It’s essential to note that labia come in various shapes and sizes, and there’s no one “ideal” appearance.
Why would someone get a labiaplasty?
There are medical reasons for labiaplasty. There are also physical, cosmetic and emotional reasons. Sometimes, labiaplasty is part of gender-affirming surgery.
Medical and physical reasons
Vaginoplasty is a surgical procedure that tightens lax vaginal muscles to achieve a narrower and tighter vaginal canal and smaller opening. This procedure can help address vaginal widening caused by aging or childbirth, which can lead to reduced sexual pleasure. The procedure typically takes 60 minutes, can be performed under general or local anesthesia, and uses a laser device for precision and minimal incisions.
- To reduce the size of your labia minora so they don’t protrude beyond the edges of the labia majora. Excess labial tissue can twist, turn, get pinched or tugged, and cause physical discomfort and irritation during exercise, physical activities (like bike riding or jogging) and intercourse.
- Decreased To improve hygiene and health since excess tissue can make cleansing more difficult and can harbor bacteria that can cause urinary tract infections (UTIs).sexual response caused by lax or stretched tissues
Labiaplasty
Labiaplasty is a cosmetic procedure that reshapes and transforms the labia minora or labia majora to address excess skin, misshapenness, or irregularities. This procedure can alleviate discomfort during sex, exercise, or wearing certain clothing. Labia reduction achieves symmetry and a more desirable shape. The procedure takes about 60 minutes, with options for general or local anesthesia. Recovery is relatively short, with most patients returning to work in 3-4 days and resuming sexual activity in 6-8 weeks.
Cosmetic and emotional reasons
- To reduce asymmetry (uneven shape) of the labia minora or labia majora when one side is longer or shaped differently.
- To improve comfort, confidence and sexual well-being about the appearance of your genitalia during intimate contact. Keep in mind that people have a variety of lip sizes and shapes, and there’s no labial appearance that’s considered normal.prove hygiene and health since excess tissue can make cleansing more difficult and can harbor bacteria that can cause urinary tract infections (UTIs).sexual response caused by lax or stretched tissues
What causes a labium to become oversized?
- Puberty can cause a growth spurt in your labia.
- Menopause or other hormonal changes can thin the tissue of your labia majora.
- Pregnancy and childbirth.
- Changes in your weight.
- Genetics.
What is the average age for labiaplasty?
Most people who have labiaplasty are between the ages of 18 and 50. But, since your labia may stretch during pregnancy and childbirth, you might want to wait until after you’re done adding to your family. A child may have labiaplasty, but only to correct problems related to daily function and activity.
What happens before surgery?
Before undergoing labiaplasty, you’ll have a thorough discussion with your surgeon about your motivations, expectations, and goals. They’ll also assess potential risks and conduct a psychological evaluation to discuss any concerns about depression and anxiety. Your surgeon will then explain the surgical details, including incision locations and expected changes to your labia. Additionally, you’ll undergo pre-surgery tests, such as blood work and imaging, and receive instructions from your surgical team to prepare for the procedure.
- What to wear to your procedure.
- When to stop food and drink.
- When to adjust or temporarily stop certain medications.
What happens on the day of surgery?
Before labiaplasty surgery, you’ll change into a surgical gown and have your vitals checked. Additional blood work and urinalysis may be performed, and an intravenous line and urinary catheter may be inserted. Your provider will then cleanse and prepare the surgical area, which may include shaving your pubic area. Anesthesia will be administered, either through IV sedation with local anesthesia or general anesthesia, depending on the procedure. Your provider will then use a scalpel, scissors, or laser to perform the surgery, choosing a technique based on the desired resizing or reshaping of your labia.
Reduction procedures
- Trim procedure. With this approach, your surgeon removes excess tissue from the outer edge of one or both sides of your labia minora so that they’re even with or inside the edges of your labia majora.
- Wedge procedure. With this approach, your surgeon removes a wedge or pie-shaped piece of tissue from the inner areas of one or both sides of your labia minora. They leave the submucosa intact so that the wrinkled edge of your labia remains intact after they stitch (suture) it. This retains a more natural look for your labia minora. Similarly, if you’re having surgery to reduce your labia majora, your surgeon removes an inner portion of each labium of your labia majora.
Enlarging procedure
To enlarge your labia majora, your surgeon takes a small amount of fat from another body area, like your abdomen or thigh (in a liposuction procedure) and injects it into your labia majora. Injecting hyaluronic acid into your labia majora is an alternative option.
What are the risks and complications of labia surgery?
- Removing too much tissue or not enough tissue.
- Bleeding.
- Bruising (hematoma).
- Infection.
- Wound breakdown.
- Ongoing pain, pain with sex or loss of sensitivity.
When will results be at their very best?
The initial swelling, soreness and temporary discoloration decrease over the first couple of weeks after surgery. Most swelling is gone after six weeks. But it may take up to four to six months of healing time for swelling to completely go away before seeing the final results of your labiaplasty. There’s usually little to no scarring.
Book Your Appointment With Us!

Understanding Acne: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
September 24, 2024

Summer Skincare Tips: How to Beat the Heat
September 24, 2024
Hydrafacial for Acne-Prone Skin
September 24, 2024
Hair Transplant Techniques: FUE vs. FUT Explained
September 24, 2024
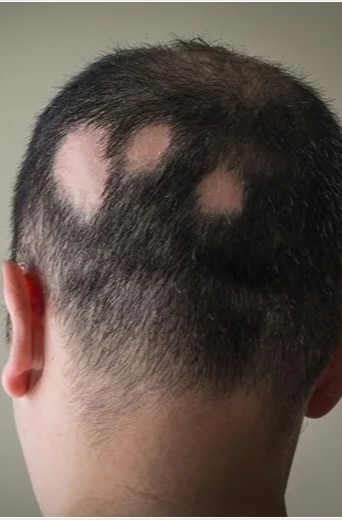
Understanding Alopecia: Types, Causes, and Treatment Options
September 24, 2024
Hydrafacial: The Ultimate Treatment for Healthy, Glowing Skin
September 24, 2024
The Importance of Regular Skin Check-Ups: Why Dr. Abbas Shah Recommends Them
September 24, 2024

Acne Treatment
September 24, 2024

Hydra Facial
September 24, 2024
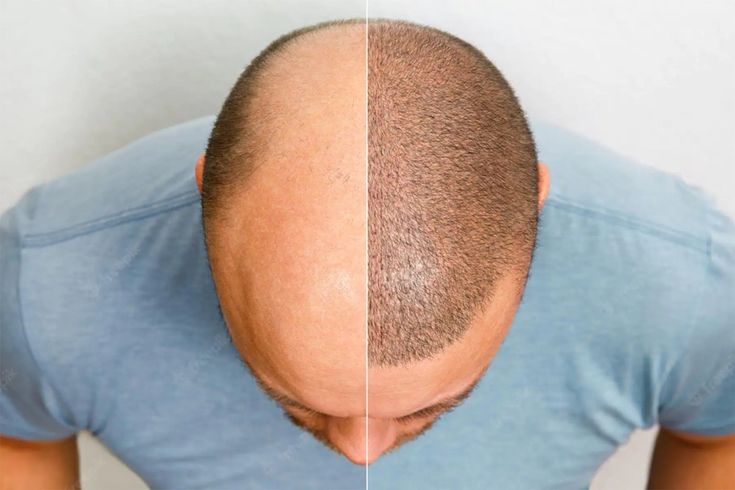
Micro Hair Transplant
September 24, 2024
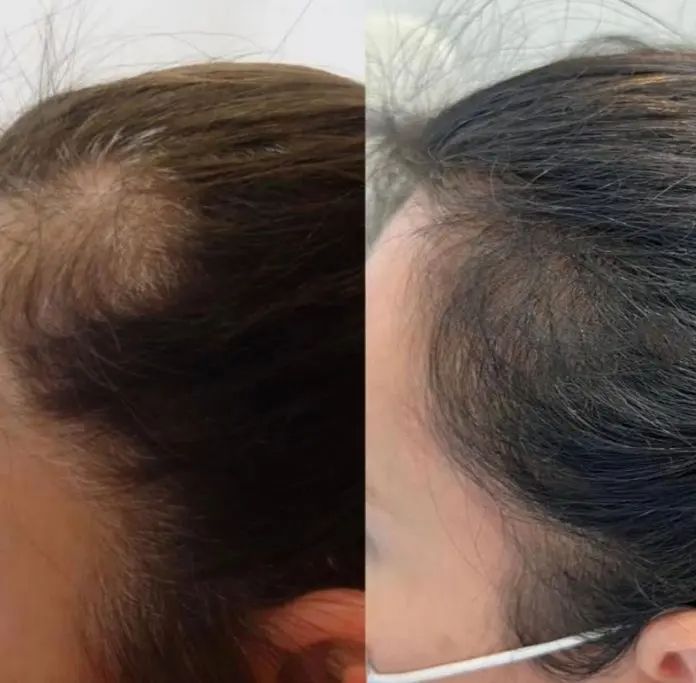
Alopecia
September 24, 2024
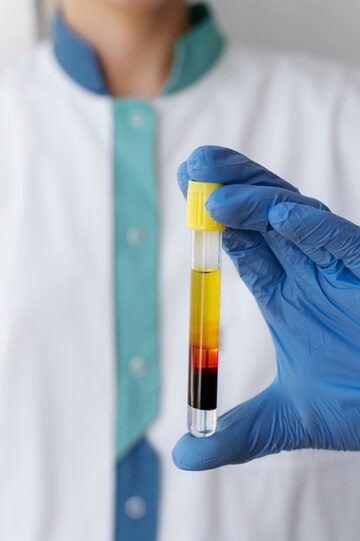
PRP Therapy
September 23, 2024
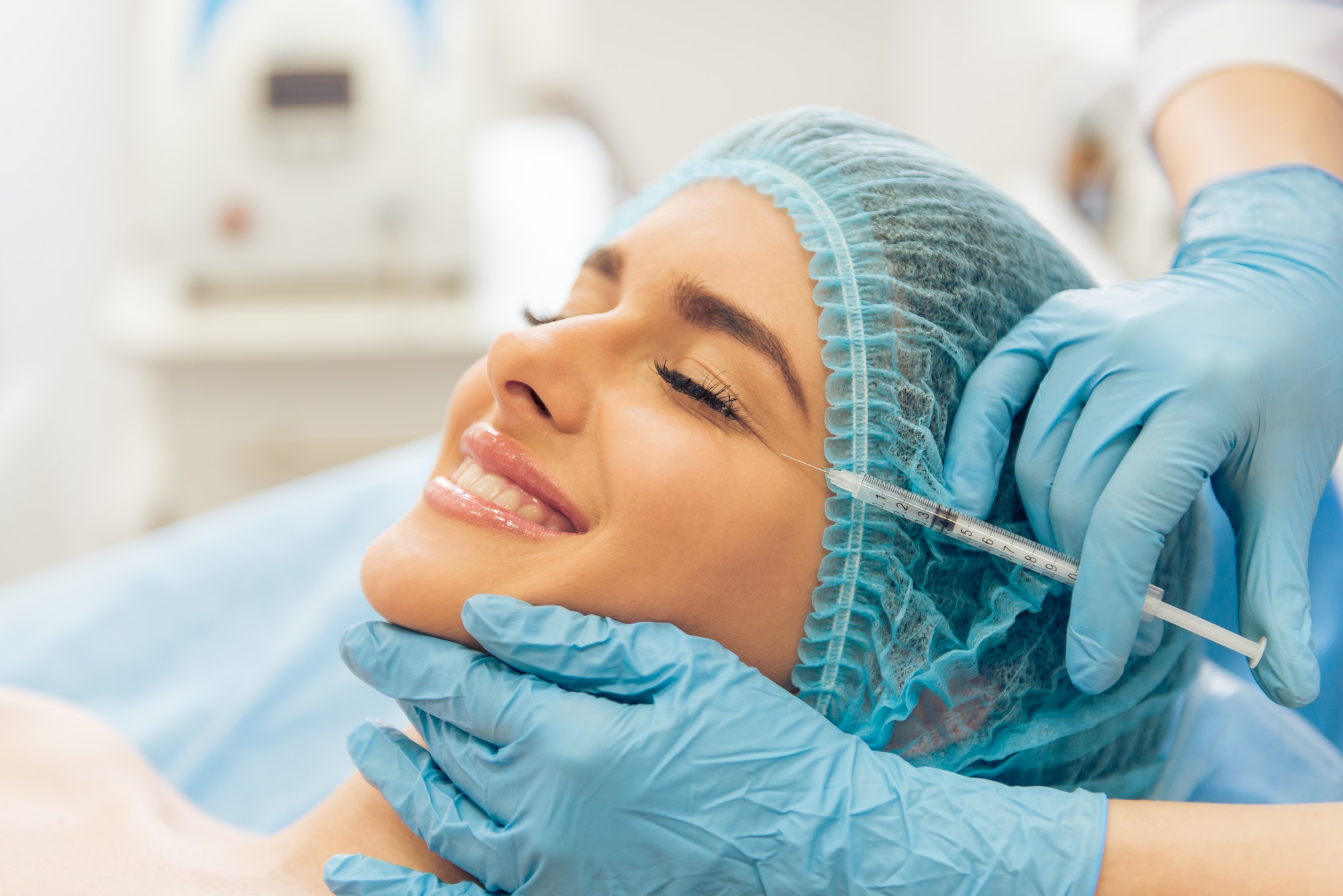
Botox
September 22, 2024
